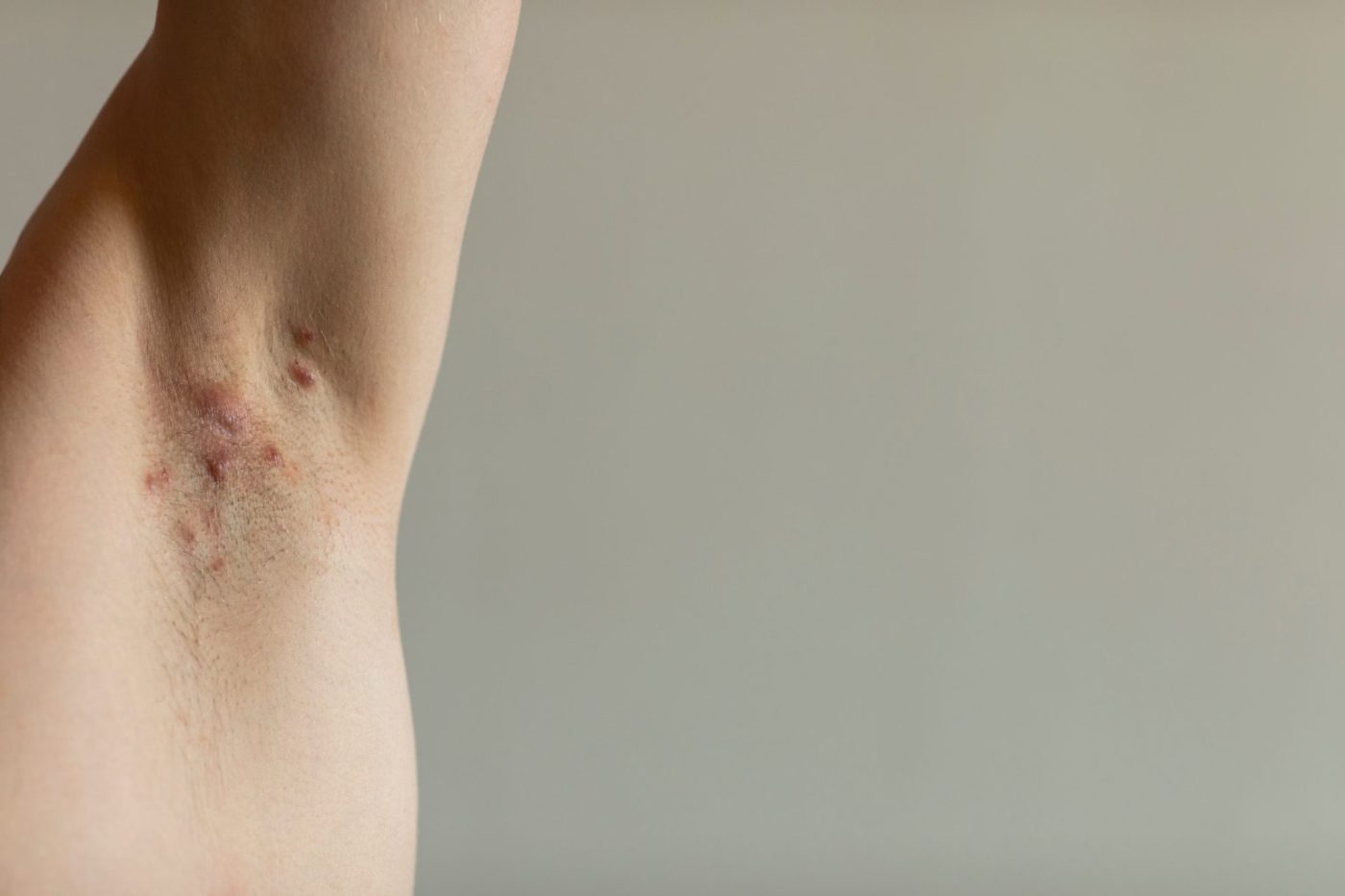
Hidradenitis suppurativa is a chronic skin condition characterized by the development of painful nodules, abscesses, and tunnels under the skin. These lesions typically occur in areas where skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts. The exact cause of hidradenitis suppurativa is not fully understood. There isn’t a cure, but treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent new boils and scarring.
Causes of hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa develops when hair follicles become blocked, but why this blockage occurs isn’t known. Experts think it could be connected to hormones, genetic predisposition, cigarette smoking or excess weight.
An infection or being unclean does not cause hidradenitis suppurativa, and it can’t be spread to other people. Hidradenitis suppurativa is a long-term skin condition that affects areas bearing apocrine sweat glands and hair follicles, such as the armpits, groin, and under the breasts. The exact cause of this condition is not known, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, immune, and environmental factors. The condition can cause painful lumps, abscesses, and scarring in the affected areas, leading to significant discomfort and reduced quality of life for those living with it. Despite the challenges it poses, hidradenitis suppurativa is not contagious, and it is important to raise awareness about this so that individuals affected by it are not stigmatized or misunderstood.
Symptoms of hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativ includese painful, pea-sized lumps or nodules under the skin. These lumps can break open and cause draining sores. Sometimes, tunnels under the skin (sinus tracts) can form and result in more severe symptoms. This chronic skin condition commonly affects areas where skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks, and under the breasts. Moreover, individuals with hidradenitis suppurativa may also experience itching, burning, and excessive sweating in the affected areas. Understanding and recognizing these symptoms is crucial for seeking timely medical attention and appropriate management of this condition.
Risk factors of hidradenitis suppurativa
- Age. The risk of hidradenitis suppurativa is higher for people in their teens and 20s.
- Sex. Females are more likely to develop hidradenitis suppurativa than males.
- Race. Ethnicity or race might affect risk level. The condition occurs most in Black people, possibly due to genetic factors.
- Family history. A tendency to develop hidradenitis suppurativa can be inherited.
- Certain conditions. Hidradenitis suppurativa is more common and severe in people who are overweight. It also has an association with severe acne, arthritis, diabetes, metabolic syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Smoking. Smoking tobacco has been linked to hidradenitis suppurativa.
How is hidradenitis suppurativa treated?
Hidradenitis suppurativa is typically treated with a combination of medical and surgical approaches. In mild cases, topical treatments such as antibiotics, corticosteroids, and antiseptics may be used to reduce inflammation and prevent infection. For more severe cases, systemic medications like oral antibiotics, retinoids, or biologic therapies may be prescribed to target the underlying causes of the condition. Surgical interventions, including drainage of abscesses, excision of affected skin areas, and laser therapy, may also be recommended to manage the symptoms and prevent recurrence. It’s important for individuals with hidradenitis suppurativa to work closely with dermatologists or healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and concerns. Regular monitoring and adjustments to the treatment approach may be necessary to effectively manage this chronic skin condition.
Complications of Hidradenitis suppurativa
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) can lead to several complications, some of which can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. One of the most common complications is the development of abscesses, which are painful, pus-filled lumps that can form in the affected areas. These abscesses can rupture and cause tunnels under the skin, known as sinus tracts, leading to the formation of more lumps and scars. In addition, HS can contribute to the development of secondary infections, such as cellulitis. Moreover, the scarring and inflammation associated with HS can restrict movement in the affected areas, leading to decreased mobility and potentially affecting daily activities. It’s important for individuals with HS to work closely with healthcare professionals to manage the condition and minimize the risk of these complications.
Leave a comment