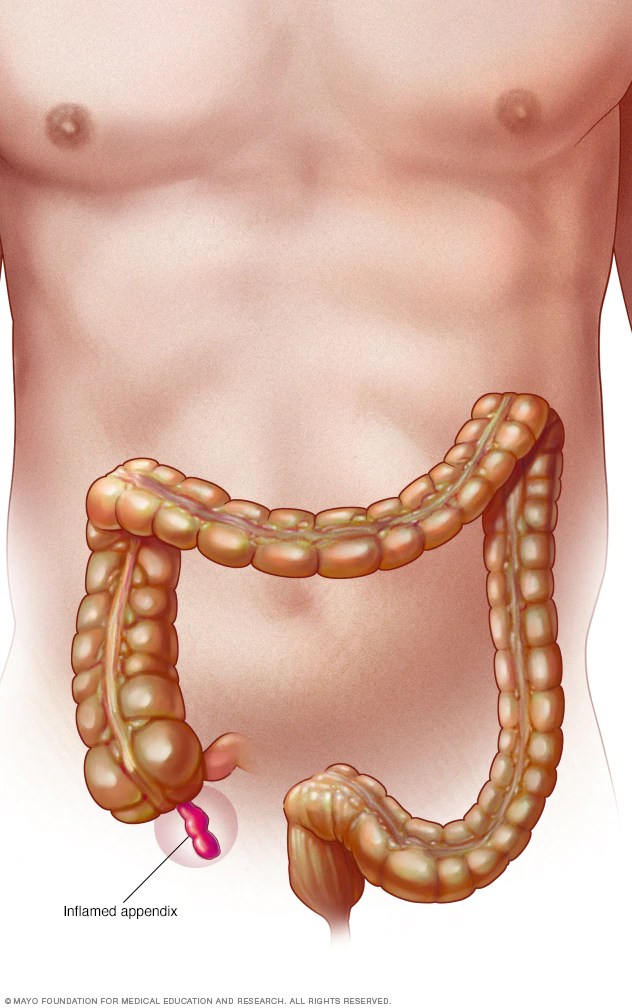
Appendicitis is a condition in which the appendix becomes inflamed. The appendix is approximately 4 inches long and it is located in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen. Bacteria can multiply inside your appendix when it becomes obstructed. This might result in the formation of pus and swelling, which can cause severe pressure in your abdomen.
What causes appendicitis?
Appendicitis occurs when the inside of your appendix becomes obstructed. Appendicitis can be caused by infection in your digestive tract such as viruses, bacteria, or parasites. It could also happen if the tube connecting your large intestine and appendix becomes blocked or clogged by stool. Tumors can occasionally cause appendicitis.
The appendix gets inflamed and enlarged as a result. As the swelling and discomfort worsen, the blood supply to the appendix is cut off. The appendix begins to die when there is insufficient blood supply. The appendix can rupture or develop holes or perforations in its walls, allowing excrement, mucus, and infection to leak through and enter the stomach. Peritonitis, a dangerous infection, can develop.
What are the symptoms of appendicitis?
- Pain that originates around your navel and frequently moves to your lower right abdomen.
- Sudden pain that begins on the right side of the lower abdomen
- Sudden pain that begins around your navel and often shifts to your lower right abdomen
- Loss of appetite
- Low-grade fever that may worsen as the illness progresses
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Abdominal bloating
- Pain that worsens if you cough, walk or make other jarring movements
- Nausea and vomiting
- Flatulence
How is appendicitis diagnosed?
- Blood tests: To check for signs of infection, such as having a high white blood cell count.
- Urine tests: To see if you have a urinary tract infection.
- Abdominal ultrasound: Lets the doctor see internal organs as they work and checks how blood is flowing through different blood vessels.
- CT scan: Shows detailed images of any part of the body, such as the bones, muscles, fat, and organs.
- MRI: Sometimes used to diagnose appendicitis, especially in a pregnant woman, instead of CT scan.
How is appendicitis treated?
Appendicitis is a serious medical condition. The appendix is likely to rupture and produce a serious, potentially fatal infection. As a result, your healthcare professional will nearly always recommend that you have surgery to remove your appendix.
Complications of appendicitis
Occasionally within 48 to 72 hours of the onset of symptoms, inflammation can lead to appendicitis and
rupture.
A rupture appendix causes bacteria, feces, and air to escape into the belly, causing infection and other potentially fatal problems.
Peritonitis, an inflammation of the abdominal lining, or an abscess can arise from a burst appendix.
Taking pain relievers has the potential to disguise symptoms and delay treatment.
Prevention of appendicitis
It is impossible to completely avoid appendicitis. But by consuming a diet high in fiber, you may be able to reduce your chance of getting IBS. Appendicitis is less frequent in nations where people consume high fiber diets, notwithstanding the need for greater study on the potential influence of nutrition.
Leave a comment