Mumps is a contagious infection caused by a virus that spreads easily through saliva and mucus.
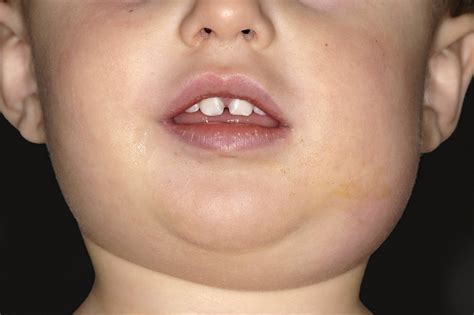
The salivary glands, commonly known as the parotid glands, are largely affected by the condition. These glands are in charge of creating saliva. On each side of your face, there are three pairs of salivary glands placed behind and below your ears. Mumps is characterized by enlargement of the salivary glands. Mumps is a common childhood infection caused by the mumps virus. Mumps has a 2-3 weeks incubation time between exposure and development of symptoms. The infection lasts typically 7-10 days
What are the symptoms of mumps?
Symptoms of mumps are often mild. Many people who get mumps do not even know that they are infected. The symptoms of mumps normally appear 2-3 weeks after the patient has been infected.
- low grade fever
- headache
- discomfort when chewing
- dry mouth
- feeling tired
- loss of appetite
What causes mumps?
Mumps is caused by the mumps virus and spreads through close contact as well as coughing and sneezing.
If you develop mumps, the virus will go from your respiratory system (nose, mouth, and throat) to your parotid glands, where it will begin to multiply. The glands become inflamed and swollen as a result of this.
The virus penetrates the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) less frequently, which is the fluid that surrounds and protects the brain and spine. Once the virus enters the bloodstream, it can spread to other organs such as the pancreas, testes (in boys and men), and ovaries (in girls and women).
How is mumps treated?
Because mumps is a virus, it doesn’t respond to antibiotics or other medications. However, you can treat the symptoms to make yourself more comfortable while you’re sick. These include:
- Drink plenty of fluids, but avoid acidic drinks such as fruit juice because these can irritate the parotid glands. Water is usually the best fluid to drink.
- Apply a cold compress to the swollen glands to help reduce the pain.
- Eat foods that do not require a lot of chewing, such as soup, mashed potatoes and scrambled eggs. Avoid sour foods as these can stimulate saliva.
- Gargle warm salt water.
- Take painkillers.
Most people who acquire the mumps will never get it again. Being infected with the virus once protects you from becoming infected again.
Complications of mumps
Mumps can occasionally cause complications, especially in adults.
- inflammation of the testicles (orchitis); this may lead to a decrease in testicular size (testicular atrophy)
- inflammation of the ovaries (oophoritis) and/or breast tissue (mastitis)
- inflammation in the pancreas (pancreatitis)
- inflammation of the brain (encephalitis)
- inflammation of the tissue covering the brain and spinal cord (meningitis)
- deafness
Prevention of mumps
The best way to prevent mumps is to be vaccinated against the disease. Most people have immunity to mumps once they’re fully vaccinated.
The mumps vaccine is usually given as a combined measles-mumps-rubella (MMR) inoculation, which contains the safest and most effective form of each vaccine
There are several steps that can be taken to help avoid the spread of infection.; these are:
- Washing hands with water and soap frequently.
- Not going into work/school until 5 days after the symptoms start.
- Covering the nose and mouth with a tissue when sneezing or coughing.
Leave a comment